Views
Definition
A view is an alternative way of representing data that exists in one or more tables or views.
A view can include all or some of the columns from one or multiple base tables, or existing views
Creating a view creates a named specification of a results table, which can be queried in the same way as a table.
You can also change the data in the base table by running insert, update, and delete queries against the view.
When you define a view, the definition of the view is stored.
The data that the view represents is stored in the base tables, not by the view itself.
You can use a view to:
- Show a selection of data for a given table, so you can omit sensitive data like tax information, birth dates, or salaries.
- Combine two or more tables in meaningful ways.
- Simplify access to data by granting access to a view without granting access to the underlying tables.
- Show only the portions of data relevant to the process that uses the view.
Create View
CREATE VIEW view_name ( col_alias1, col_alias2, col_alias3...) #<columns used as input>
AS SELECT col1, col2, coln #<cols of the view>
FROM table_name
WHERE condition if any;
# Then you can query the view as you would any table
SELECT *
FROM view_name;Syntax: CREATE VIEW statement and assign a name (up to 128 characters in length) to the view.
- List the columns that you want to include. You can use an alias to name the columns if you wish.
- Use the AS SELECT clause to specify the columns in the view, and the
- FROM clause to specify the base table name.
- You can also add an optional WHERE, GROUP BY, HAVING clause to refine the rows in the view.
- CANNOT use ORDER BY
Drop View
To remove a view use:
DROP VIEW view_nameMySQL View
We’ll use MySQL on the IBM cloud.
- Open phpMyAdmin
- Create db: HR
- Import HR_Database_Create_Table_Script.sql from local drive
- Now you can see the 5 tables in the folder tree
- Download csv data files to local drive
- Select each table at a time from the left menu
- Verify that all column headings have been imported
- Import Tab -> To import the data to each table
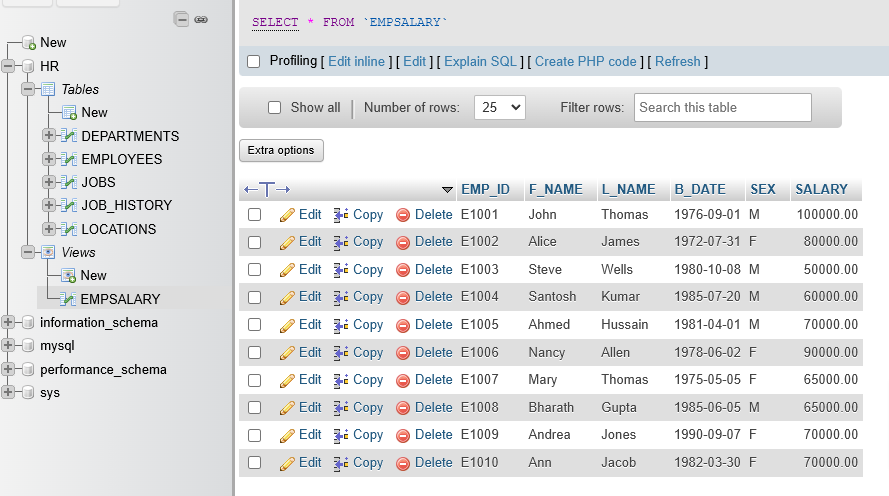
Create View 1
Click on SQL Tab and enter this
CREATE VIEW EMPSALARY AS
SELECT EMP_ID, F_NAME, L_NAME, B_DATE, SEX, SALARY
FROM EMPLOYEES;- You will see a new view appear under Views in the left side Folder Tree
- Click on EMPSALARY
- A view of the view will appear
Update View 1
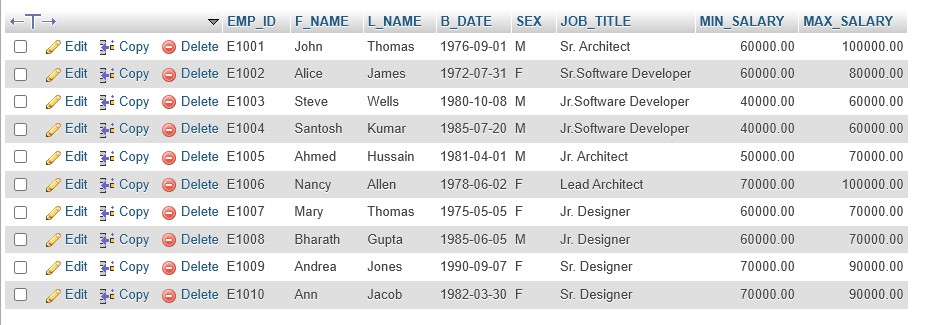
Assume that the EMPSALARY view we created doesn’t contain enough salary information, such as max/min salary and the job title of the employees. For this, we need to get information from other tables in the database.
- You need all columns from
EMPLOYEEStable used above, except forSALARY - You also need the columns
JOB_TITLE,MIN_SALARY,MAX_SALARYof theJOBStable
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW EMPSALARY AS
SELECT EMP_ID, F_NAME, L_NAME, B_DATE, SEX, JOB_TITLE,MIN_SALARY, MAX_SALARY
FROM EMPLOYEES, JOBS
WHERE EMPLOYEES.JOB_ID = JOBS.JOB_IDENT;Implicit inner join.
We just used implicit inner join. Let’s say we are combining the data of two different tables, EMPLOYEES and JOBS by connecting their respective columns JOB_ID and JOB_IDENT, since both the columns contain common unique data.
Drop View 1
DROP VIEW EMPSALARY;And you’ll notice the directory Views is removed from the tree since it only contained the one view we had created above.
Create View 2
CREATE VIEW EMP_DEPT AS
SELECT EMP_ID, F_NAME, L_NAME, DEP_ID
FROM EMPLOYEES;Update View 2
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW EMP_DEPT AS
SELECT EMP_ID, F_NAME, L_NAME, DEP_NAME
FROM EMPLOYEES, DEPARTMENTS
WHERE EMPLOYEES.DEP_ID = DEPARTMENTS.DEPT_ID_DEP;Drop View 2
DROP VIEW EMP_DEPTSummary
| Topic | Syntax | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create View | CREATE VIEW view_name AS SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name WHERE condition; |
A CREATE VIEW is an alternative way of representing data that exists in one or more tables. |
CREATE VIEW EMPSALARY AS SELECT EMP_ID, F_NAME, L_NAME, B_DATE, SEX, SALARY FROM EMPLOYEES; |
| Update a View | CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW view_name AS SELECT column1, column2, ... FROM table_name WHERE condition; |
The CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW command updates a view. |
CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW EMPSALARY AS SELECT EMP_ID, F_NAME, L_NAME, B_DATE, SEX, JOB_TITLE, MIN_SALARY, MAX_SALARY FROM EMPLOYEES, JOBS WHERE EMPLOYEES.JOB_ID = JOBS.JOB_IDENT; |
| Drop a View | DROP VIEW view_name; |
Use the DROP VIEW statement to remove a view from the database. |
DROP VIEW EMPSALARY; |