Big Data Basics
Mapreduce
A programming model for processing large data sets. Think of it as an API, an algorithm or a way of breaking up data sets and processing them in a distributed manner.. It offers a way to horizontally scale data analysis problems. It consists of a mapper and a reducer. Google invented and first used it for web crawling, page rank, Yahoo, Ebay, Amazon, Facebook (which contributed Hive)
Mapper
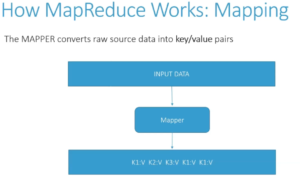
Mapper is a function that parses source data and maps values to unique keys, so it extracts the information you care about from your data set and organizes it for you. Various parts of your data may go to different mappers which can process them in parallel on different computers. So for example
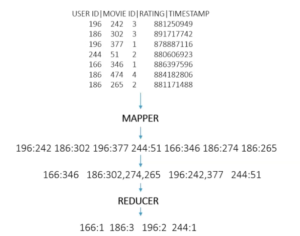
- If we use the movie lens data set and we want to see how many movies did each user rated
- In other words, we want to extract each unique user, or The KEY = User ID – For each unique UserID we want to find out the movies they rated. Because each user could have rated many movies
- And Map each Unique ID=KEY to the Movie ID value
- So the Mapper would provide us with the Values(MovieID) for Each Key(UserID)
- Here is the outcome which is the job of the mapper – which is to extract and organize what we care about. Kinda like a sort and grouping in python, so what it does automatically is group and sort the mapped data and we end up with this before it is sent to the Reducer

- So now it has consolidated all of those values together and then it sends each key to the reducer along with a function or an order of what to do with the keys, in this case we want to find out how many movies each user has rated so we just issue a function LEN() with would be the length of each key. So see below what the Reducer will output
Reducer
Processes all the values for a given key. So after the mapper is done, all the values for each key are sent to a reducers which then processes all that information for each key.
Horizontal Scaling
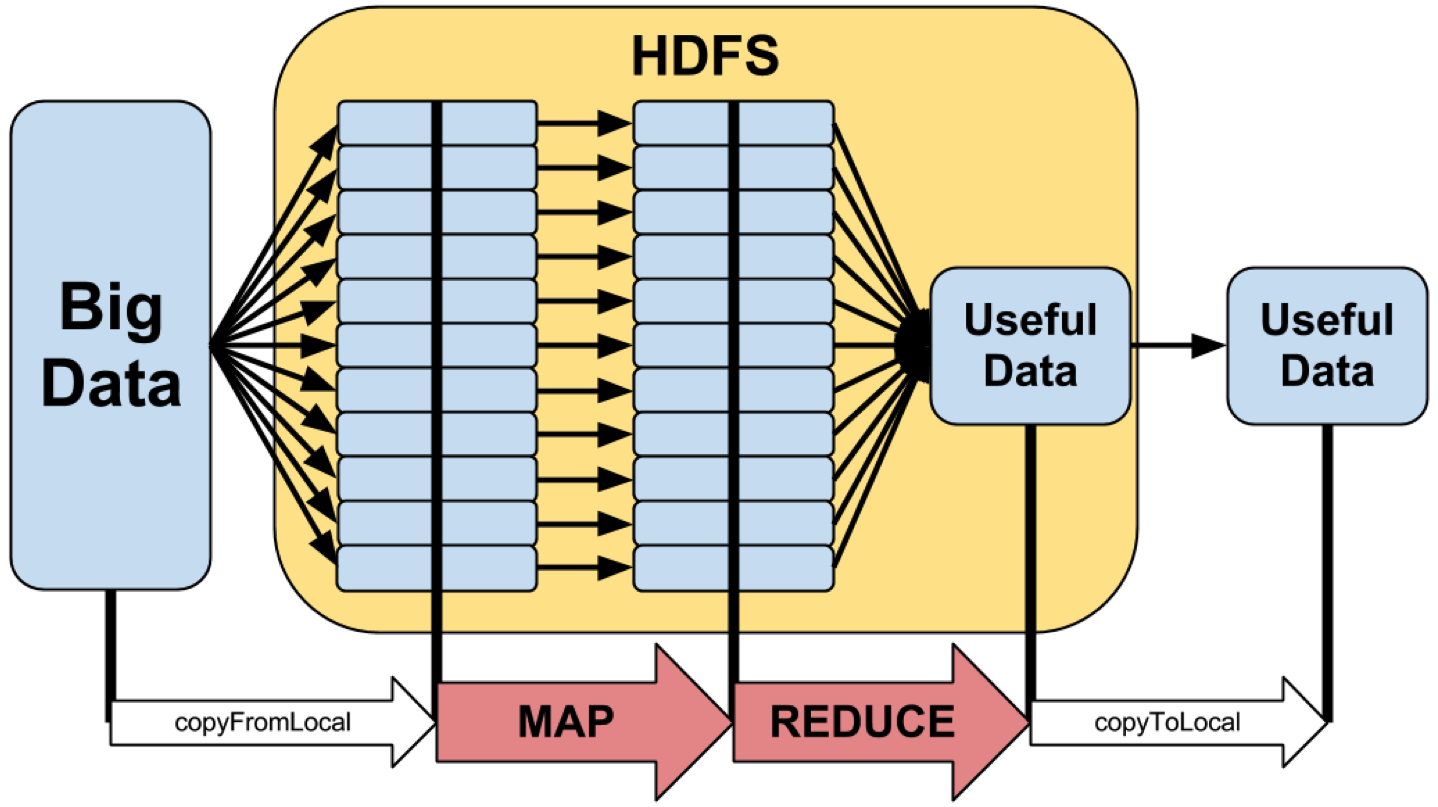
Its programming model lends itself well to distributing it throughout multiple computers on a large cluster. So HS has unlimited upward potential while you can add as many computers as you want to a cluster, hundreds, thousands…. till you get the job done. It does take skills to make those computers to communicate with each other, it scales much more widely than vertical scaling would. So MapReduce offers a programming model for distributing the processing of a large data set among multiple computers
Vertical Scaling
VS would be if you just kept adding more resources to one computer so if the data analysis job is too large for one computer, you just keep adding more processors and memory and other resources on top of that computer till you are able to do the job.
Hadoop
Is a software that manages applications that run on a cluster of computers (like MapReduce). It manages the cluster for you. It makes sure all your data is distributed and is where it is supposed to be. It offers HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System)- see below. Hadoop also manages all the communication between computers through a technology called YARN – see below. It also gives you fault-tolerance, so it not only allows you horizontal scaling, but the more you computers you add the higher the probability that one will fail while processing a job. So Hadoop can actually duplicate your data across multiple machines in your cluster and that way if one of your computers goes down you know which computer to to instead to retrieve the backup copy and continue the process as if nothing happened.
HDFS
It’s the mechanism for sharing files across the cluster in a reliable manner. So if you have a large data sets, all your nodes on your computer cluster need to access that data somehow and then need to write the results someplace as well and that’s where HDFS comes into play.
Yarn
Communication between computers and keeps track of what information is where, and what information goes where and on which cluster and how they communicate with each other to coordinate their results.